InnoDB锁类型
InnoDB锁类型
- Shared and Exclusive Locks
- Intention Locks
- Record Locks
- Gap Locks
- Next-Key Locks
- Insert Intention Locks
- Auto-inc Locks
InnoDB - S&X Lock
-
Row-Level Locking
-
S Locks (shared locks)
- A shared (S) lock permits the transaction that holds the lock to read a row
- Example: select * from xx where a=1 lock in share mode
-
X Locks ( Exclusive Locks)
- An exclusive (X) lock permits the transaction that holds the lock to update or delete a row.
- Example:select * from xx where a=1 for update
-
S 和 S 兼容, X 和 S 互斥, X和X互斥
-
InnoDB - S&X Locks举例
-
select * from t where i=1 lock in share mode
-
select * from t where i=1 for update
-
如何查看SQL加锁信息?
-
进⾏如下设置可以看到此SQL持有锁信息 SET GLOBAL innodb_status_output=ON; SET GLOBAL innodb_status_output_locks=ON;
5.6.16版本引⼊此参数,影响性能,谨慎操作
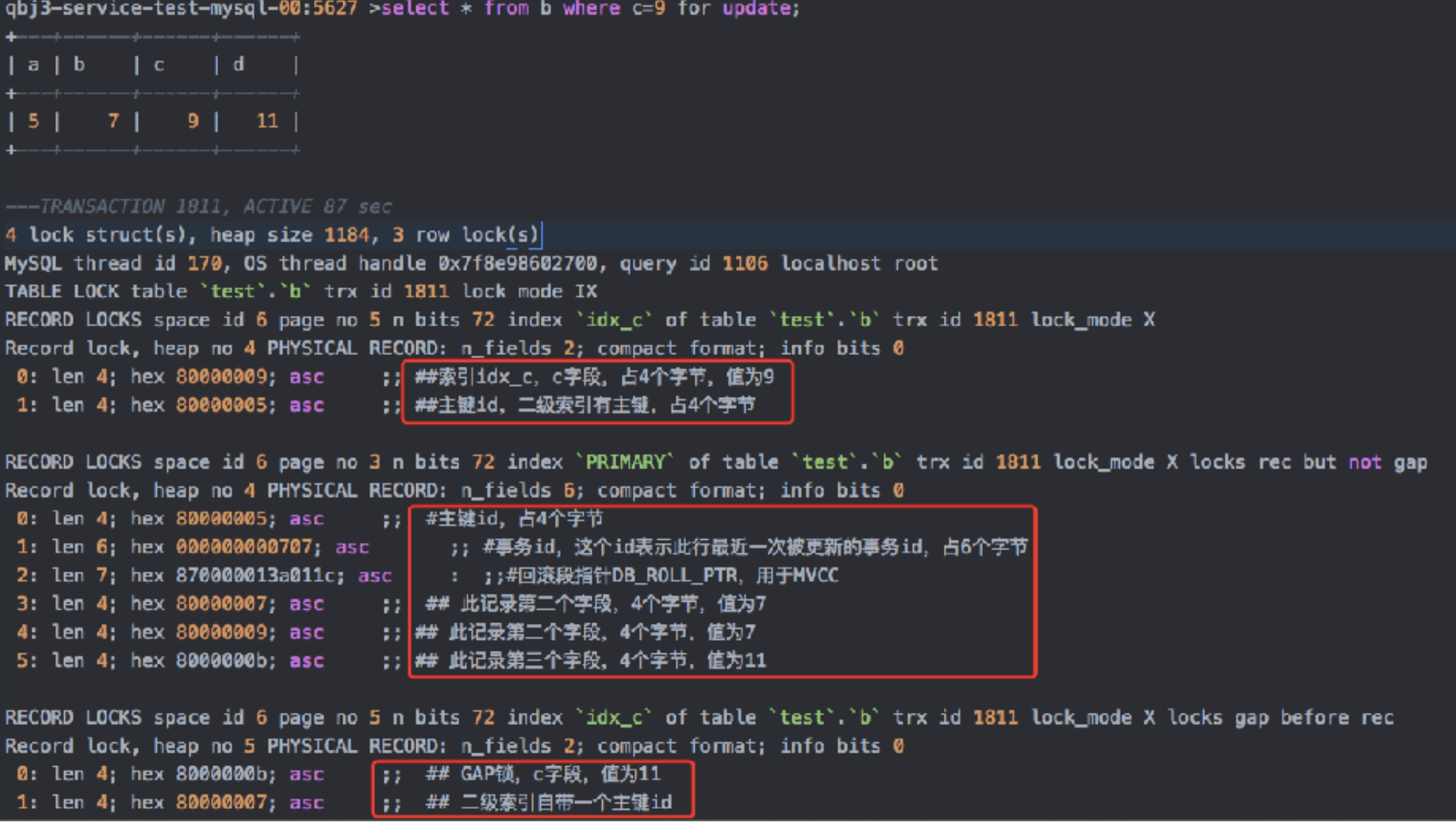
-
InnoDB - Intention Locks
- InnoDB⽀持多粒度锁,允许⾏锁和表锁并存
- Table-Level Locks
- Intention shared Lock(IS) 意味着事务需要在表的⾏上⾯添加S锁,因此获取S锁之前需要获取IS锁
- Intention exclusive Lock(IX)意味着事务需要在表的⾏上⾯添加X锁,因此获取X锁之前需要获取IX锁
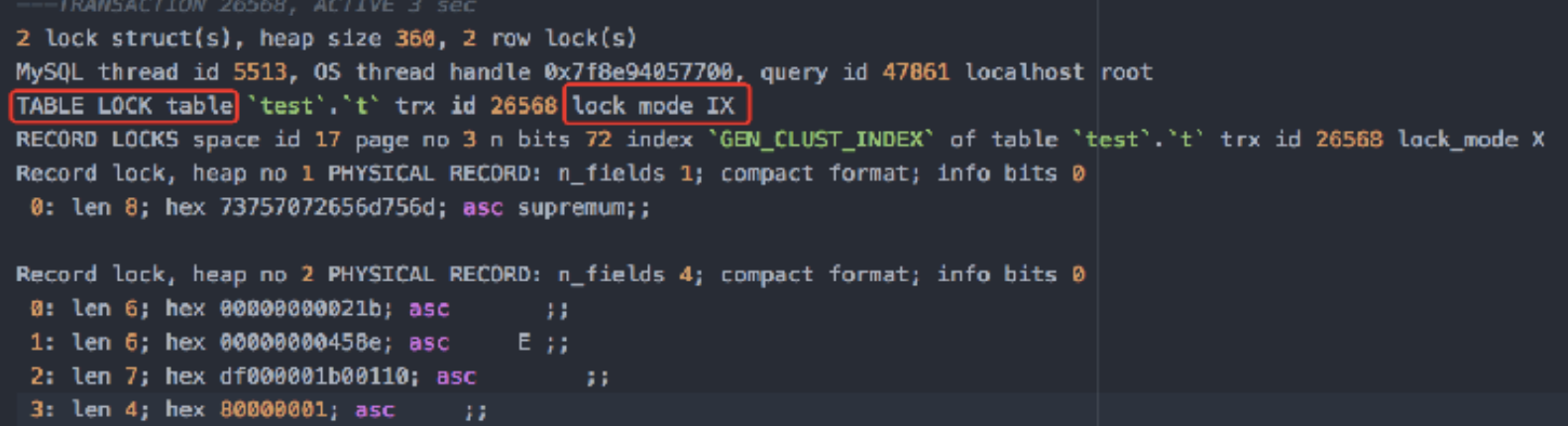
- InnoDB兼容性
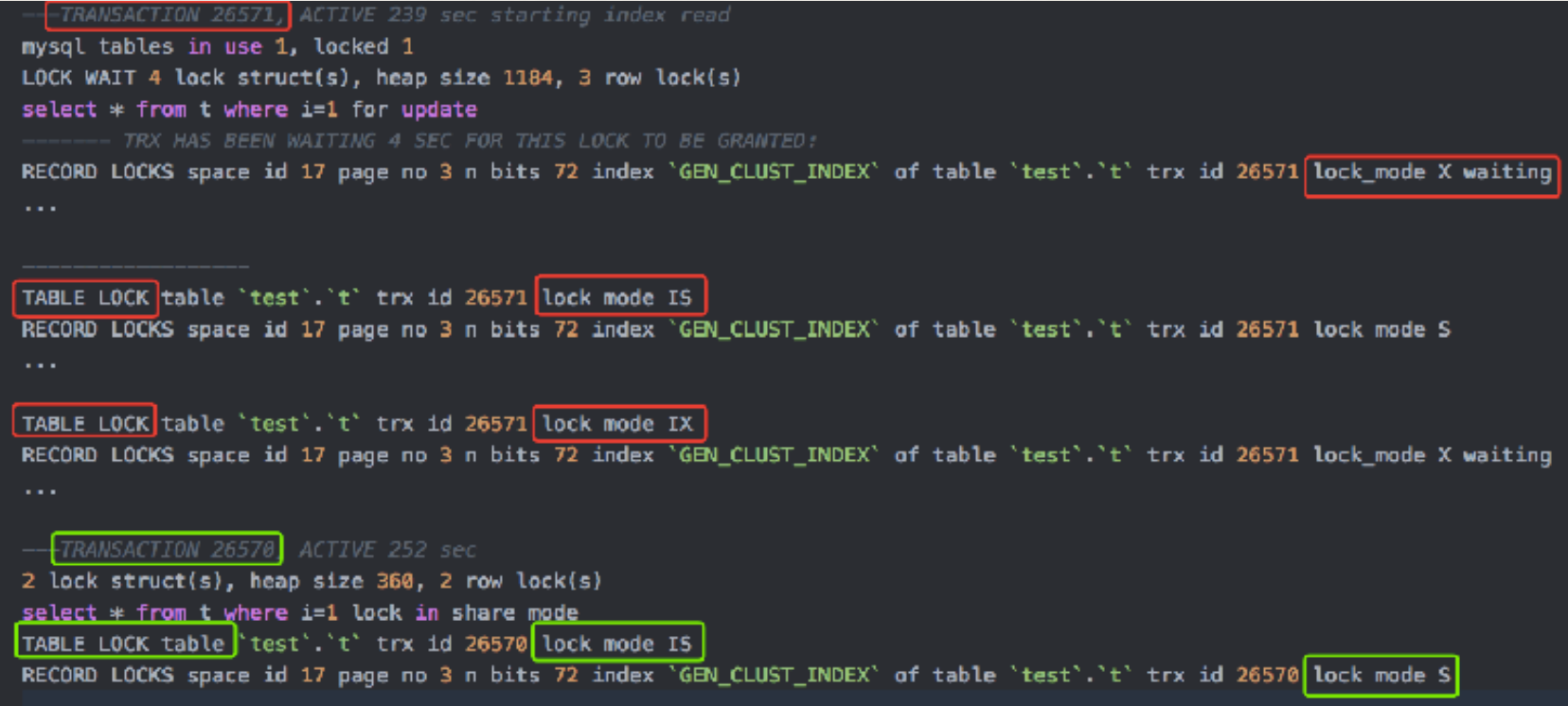
| X | IX | S | IS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | conflict | conflict | conflict | conflict |
| IX | conflict | compatible | conflict | compatible |
| S | conflict | conflict | compatible | compatible |
| IS | conflict | compatible | compatible | compatible |
InnoDB - Record Locks
- 记录锁是对索引加锁,⽽不是具体的数据⾏
- 即使表没有定义索引, InnoDB产⽣隐藏聚簇索引⽤于加锁
InnoDB - Gap Locks
- A gap lock is a lock on a gap between index records, or a lock on the gap before the first or after the last index record
- A gap might span a single index value, multiple index values, or even be empty.
- Gap可能通过设置Read-Commited以及 innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog进⾏显⽰关闭
InnoDB - Next-Key Locks
-
A next-key lock is a combination of a record lock on the index record and a gap lock on the gap before the index record
-
InnoDB 默认的事务隔离级别是REPEATABLE READ
-
在RR模式下, InnoDB 使⽤ next-key locks 防⽌幻读
- InnoDB - Next-Key Locks举例
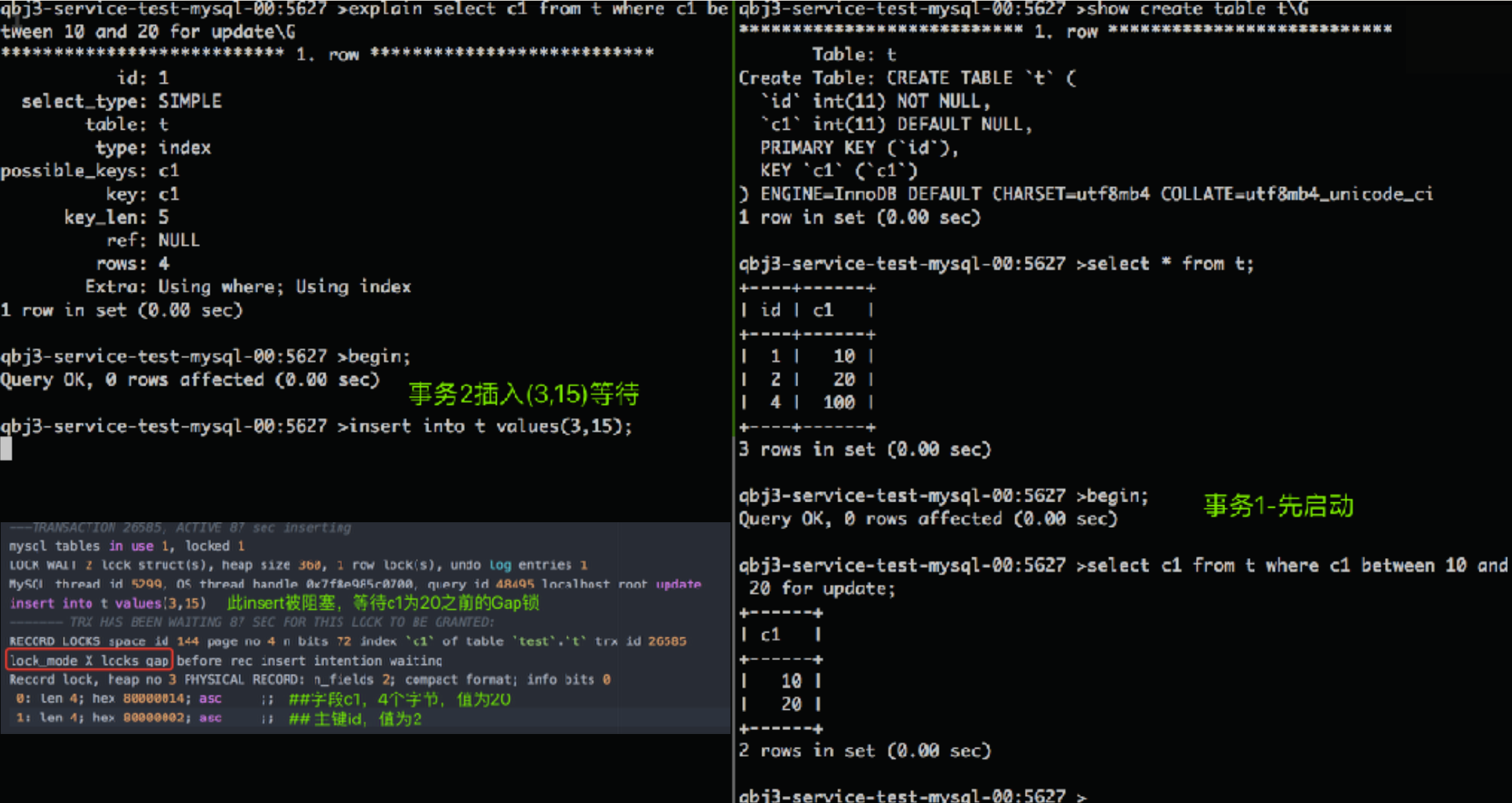
- InnoDB - Next-Key Locks举例
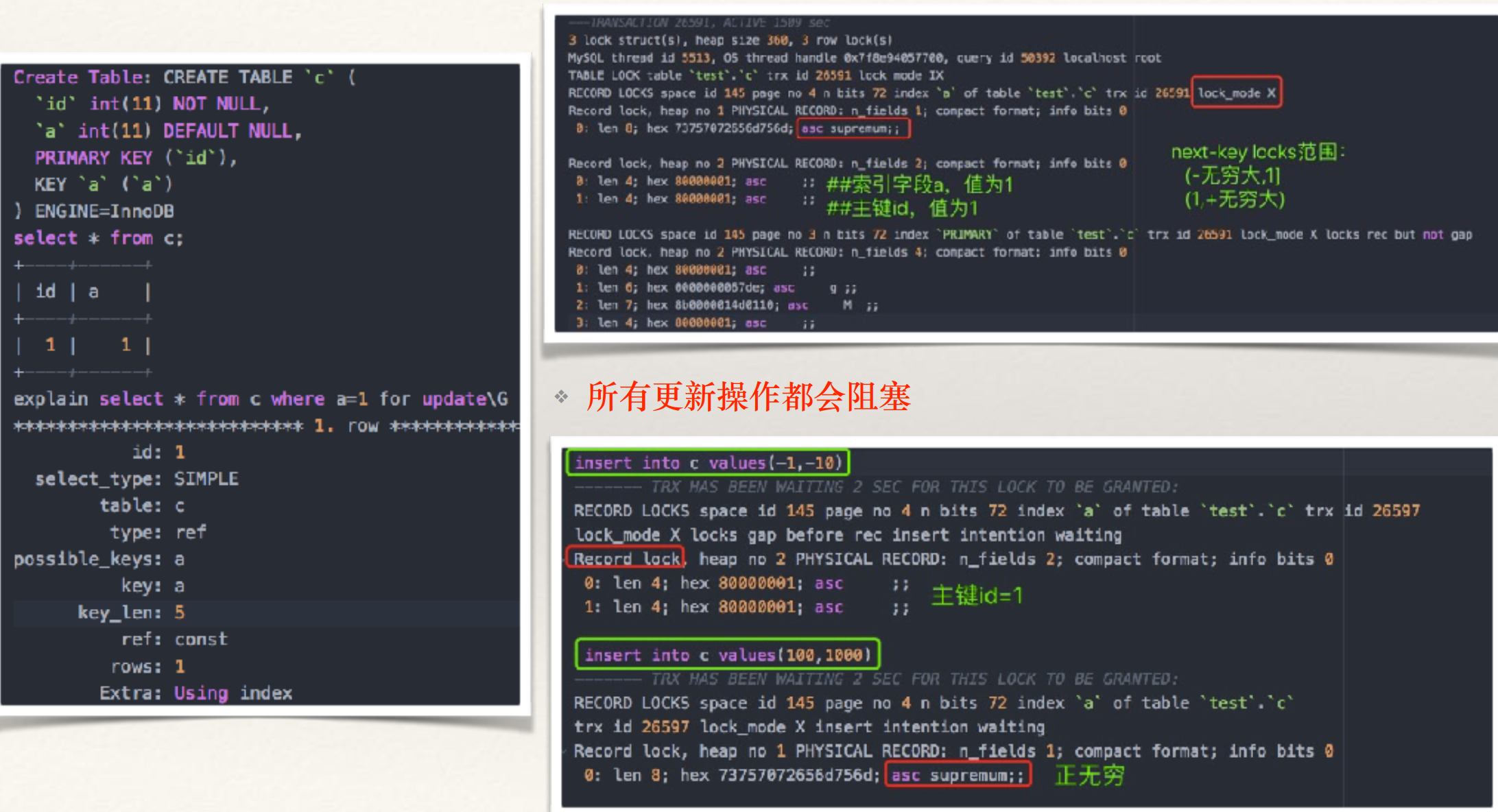
- InnoDB - Next-Key Locks举例
InnoDB - Insert Intention Locks
-
An insert intention lock is a type of gap lock set by INSERT operations prior to row insertion

InnoDB - AUTO-INC Locks
-
特殊的table-level lock
-
持有时间在当前sql执⾏完成就释放,⽽不是事务结束后才释放
-
通过参数innodb_autoinc_lock_mode控制,具体有三种模式
-
AUTOINC_OLD_STYLE_LOCKING (0)
-
AUTOINC_OLD_STYLE_LOCKING (1) 默认模式,保证ID连续
-
AUTOINC_NO_LOCKING (2)
- 只在分配时加个mutex即可很快就释放
- 在statement格式下不能保证批量插入的复制安全性
- 更快
-
InnoDB MVCC
-
相对于基于锁的协议, MVCC最⼤好处: 读不加锁,读 写不冲突
-
多版本控制
-
读操作
-
快照读(snapshot read)
- 快照读:简单select操作, 不加锁
-
当前读(current read)
-
特殊读操作,插⼊/更新/删除, 需要加锁
- select * from table where ? lock in share mode
- select * from table where ? for update
- insert into table values (…)
- delete from table where ?
- update table set ? where ?
-
-
-
InnoDB MVCC实现关键点
-
ROW记录格式
- DB_TRX_ID 表示记录最后一次被更新的trxID
- DB_ROLL_PTR 回滚指针,指向undo(update前的版本)
- DB_ROW_ID,只出现在聚簇索引中
-
ROW和Undo关系
- 通过回滚段实现多个版本的读取
-
ReadView判断
-
通过⾼低⽔位判断读取的版本
-
活跃事务(未提交的事务)
-
Read-View为活跃事务列表
-
low_limit_id 高⽔位
- 当前读看不到⼤于此id的trx修改值
-
up_limit_id 低⽔位
- 当前读可以看到所有⼩于此id的trx修改值
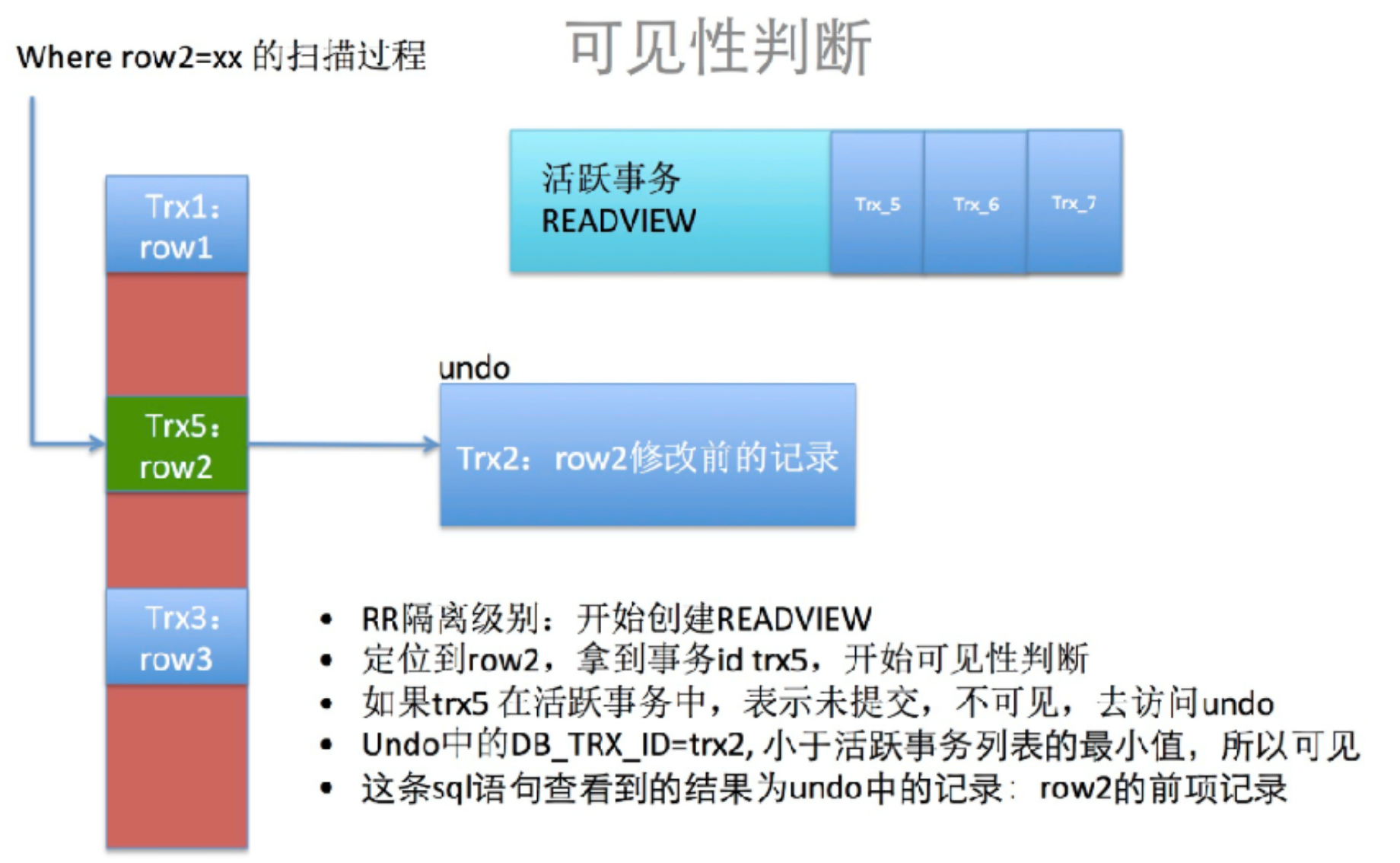
-
-
事务隔离级别
-
Read Uncommitted
- 可以读取未提交的事务,此隔离级别不会使⽤。
-
Read committed (RC)
- 针对当前读, RC隔离级别保证对读取到的记录加锁(⾏锁),存在不可重复读/幻读现象。
-
Repeatable Read(RR)
- 针对当前读, RR保证对读取到的记录加锁(⾏锁),同时保证对读取的范围加锁,新的满⾜查询条件的记录不能够插⼊(Next-Key Locks),不存在幻读现象
-
Serializable
- 从MVCC并发控制退化为基于锁的并发控制。所有的读操作都为当前读,读加读锁(S锁),写加写锁(X锁)。 Serializable隔离级别下,读写冲突,并发急剧下降
读现象问题
-
丢失更新 (事务ACID保证不会发⽣)
-
脏读
- 当⼀个事务允许读取另⼀个事务修改但未提交的数据时,就可能发⽣脏读
-
不可重复读
- 在⼀次事务中,当⼀⾏数据获取两遍得到不同的结果表⽰发⽣了“不可重复读“
-
幻读
- 不可重复读的⼀种特殊场景。当事务1两次执⾏SELECT ... WHERE检索⼀定范围内数据的操作中间,事务2在这个表中创建了(如INSERT)⼀⾏新数据,这条新数据正好满⾜事务1的“WHERE”⼦句。